Common types of injection molding materials Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that allows for the production of intricate and detailed parts from various materials. Understanding the different ty
Assist global clients in engineering material,professional custom injection molding service,CNC machining service.We can provide you with one-stop solutions.
Those plastics materials like UHMW-PE , MY Nylon , PA6 , POM , HDPE , ABS , PU , PC , PVC, PP , PET , PBT , Acrylic , PEEK , PPS , PTFE , PVDF , PAI , PEI , PSU , PI , PBI etc., they have different characteristic ! For example flowing temperature , crystallization speed , heat dispense , viscosity , pressure, speed , deformation and stripping .
Thanks for clients all along support , we gain lots of successful and failure cases , those experiences we store in database , which guide our new staff avoid same mistake. Today our comprehensive service from industrial design, mold design and manufacturing, volume production and production is based on an end-to-end quality assurance system that delivers an efficient, cost-saving, turnkey solution in plastic injection molding manufacturing.
Our mold team uses the lasted new version software design programs: UG, ProE, SolidWorks, Catia, Rhino etc., you can send any type of drawings xmt,step,vad or .iges. We also give you service is reverse engineering, we can follow your sample to create a completely new 3d drawings and the molds.
Our clients include medical industry, automobile, electronics industry, consume plastic products, etc., Our skilled technician and mould maker specialists work with each individual client and use the best material available for each application, Guides your project through each phase of development to save you time and money. We will explain whole process efficiently in five main stages: the production of the technical preparation stage, the preparation stage of raw materials, parts and components processing stage, assembly and commissioning phase trial identification stage. It is clear and confident to achieve success .
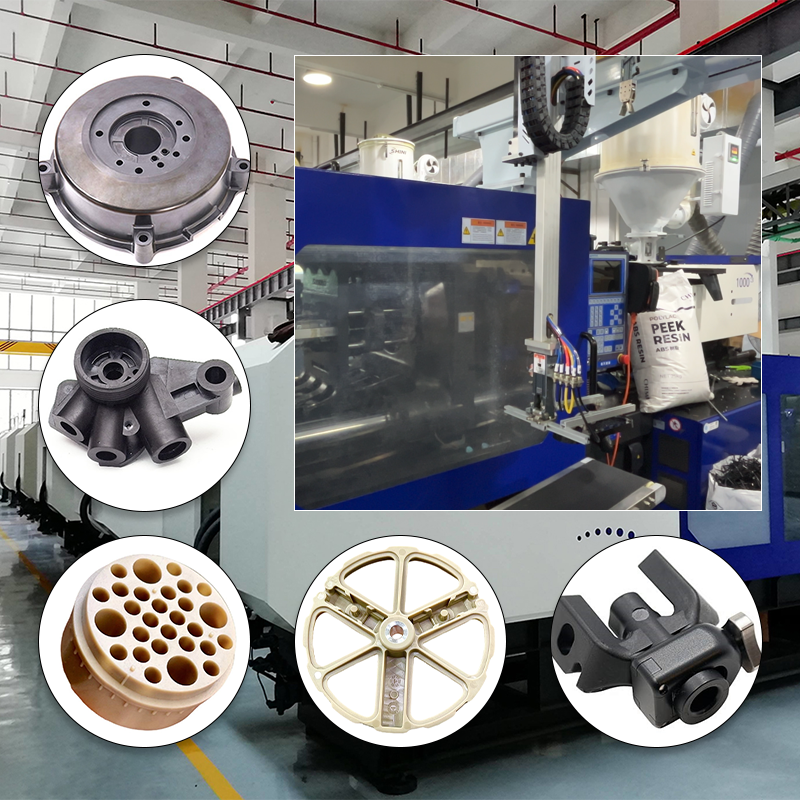
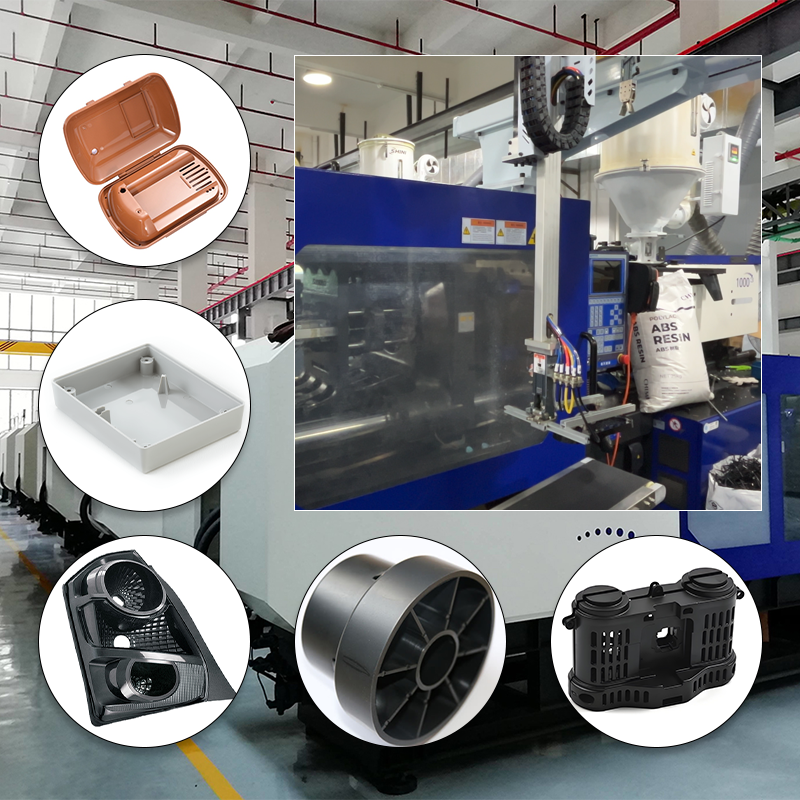
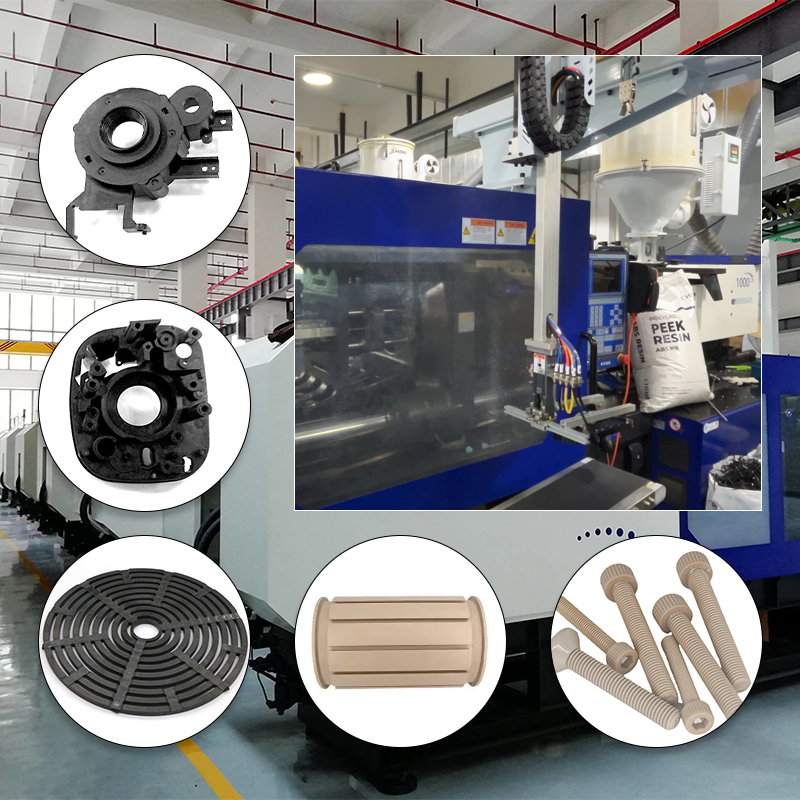
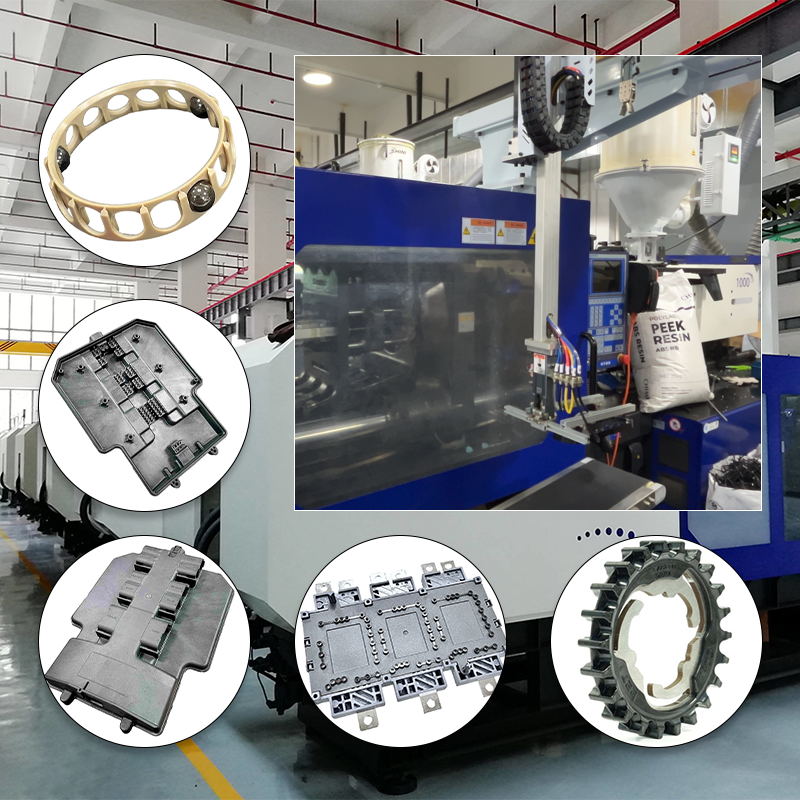







Common types of injection molding materials
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that allows for the production of intricate and detailed parts from various materials. Understanding the different types of injection molding materials is crucial for manufacturers, designers, and engineers alike. The most common categories of materials used in this process include thermoplastics, thermosetting polymers, elastomers, and bioplastics, each offering unique characteristics and advantages.
Thermoplastics are perhaps the most widely utilized materials in injection molding. They are characterized by their ability to be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing any chemical change. This property makes thermoplastics highly versatile, allowing them to be molded into complex shapes with high precision. Some popular thermoplastics include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polycarbonate (PC), and polypropylene (PP). Each of these materials possesses distinct properties that make them suitable for various applications, ranging from consumer goods to automotive components.
On the other hand, thermosetting polymers differ significantly from thermoplastics in their behavior during the molding process. Once set, these materials cannot be remelted or reshaped. Instead, they undergo a chemical reaction that transforms them into a rigid structure. Common examples of thermosetting polymers include epoxy resins, phenolic resins, and polyurethane. These materials are known for their excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and stability under extreme conditions.
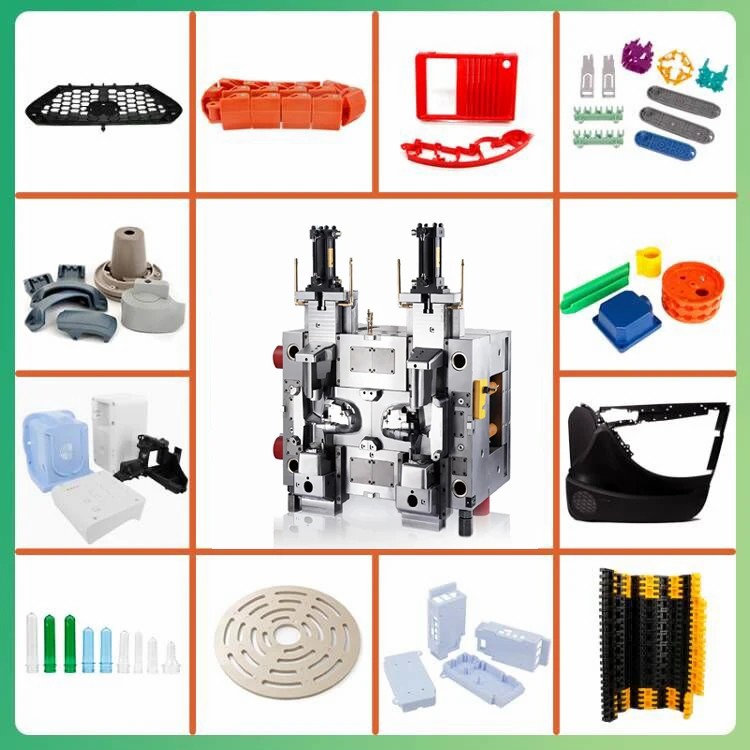

Specialty materials for specific applications
In addition to common thermoplastics and elastomers, the injection molding industry also utilizes a range of specialty materials tailored for unique applications. These materials often possess enhanced properties that make them suitable for specific requirements or challenging environments. Examples of specialty materials include high-performance polymers, conductive plastics, and flame-retardant materials, each designed to meet the demands of their respective applications.
High-performance polymers, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and polyphenylene sulfide (PPS), are known for their exceptional thermal resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability. These materials are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications where performance under extreme conditions is necessary. Their ability to withstand high temperatures and harsh chemicals makes them ideal for components like bearings, seals, and insulators.
Conductive plastics are another category of specialty materials that have gained prominence in recent years. These materials incorporate conductive fillers, such as carbon black or metal fibers, to impart electrical conductivity. Conductive plastics are primarily used in applications like electronic enclosures, automotive components, and shielding materials, where electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection is essential. The versatility of conductive plastics allows manufacturers to design lightweight and cost-effective solutions for complex electronic systems.
Flame-retardant materials are specifically engineered to reduce the flammability of plastic components, making them crucial for applications in industries such as construction, automotive, and electronics. By incorporating flame-retardant additives, manufacturers can enhance the safety of their products while complying with regulatory requirements. These materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet the necessary flame resistance standards, offering peace of mind for end-users.